The goal here is to detect groups of genes that demonstrate similar expression patterns and are also highly connected in a given interactions network.
In order to operate these tools, an interactions network in .SIF format needs to be loaded. This can be done either by selecting Data>>Load Network… or via the dialog boxes of the tools.
In order to perform network based grouping Expander incorporates two algorithms: Matisse and Degas (for details see the References section). The DEGAS algorithm is relevant when the expression dataset compares two groups of heterogeneous samples (as in case-control studies). The groups detected by these tools are referred to as “modules” and may contain also genes that exist in the network, but are not present in the filtered GE data (referred to as “Back nodes”).
To use the more advanced, stand-alone versions of MATISSE and DEGAS (with higher flexibility), please refer to the Matisse home page.
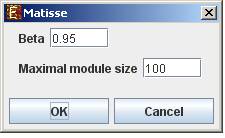
In order to apply the Matisse algorithm to the data select Unsupervised Grouping>>Network >>Matisse. The following dialog box will appear:

It enables the configuration of some of the parameters for the algorithm:
|
Field |
Description |
|
Beta |
The fraction of gene pairs that are expected to be strongly co-expressed in each module |
|
Maximal module size |
The maximum size for a detected module. |
Upon clicking ‘OK’ in the dialog box, the Matisse algorithm is operated on the dataset.
In order to apply the Degas algorithm to the data select Supervised Grouping>>Network >>Degas. The following dialog box will appear:
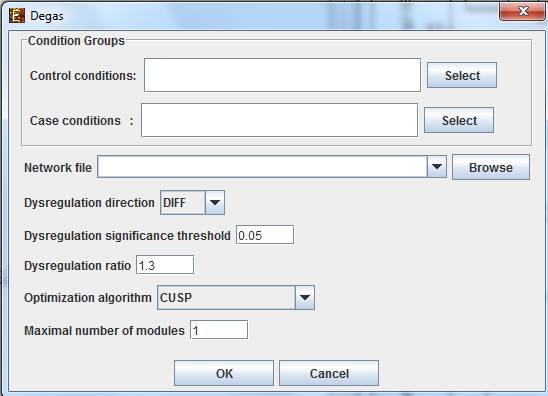
It enables the configuration of some of the parameters for the algorithm:
|
Field |
Description |
|
Case conditions |
The case conditions |
|
Control conditions |
The control conditions |
|
Dysregulation direction |
This parameter will determine which direction of dysregulation will be sought (up/down-regulation/both). |
|
Dysregulation significance threshold |
This threshold will be used to identify which genes are differentially expressed in each 'case' sample compared to the controls |
|
Dysregulation ratio |
The minimal threshold for the ratio between the gene expression in any of the case conditions and the average expression in the control conditions. Above this threshold a case condition is designated as dysregulated. |
|
Optimization algorithm |
The algorithm used to identify dysregulated pathways (DPs). See the DEGAS manuscript for details. CUSP is the recommended option |
|
Maximal number of modules |
After DEGAS identifies a significant DP, it removes it from the input data and attempts to identify additional DPs. This parameter specifies the total number of DPs that will be sought. |
Upon clicking ‘OK’ in the dialog box, the Matisse algorithm is operated on the dataset.
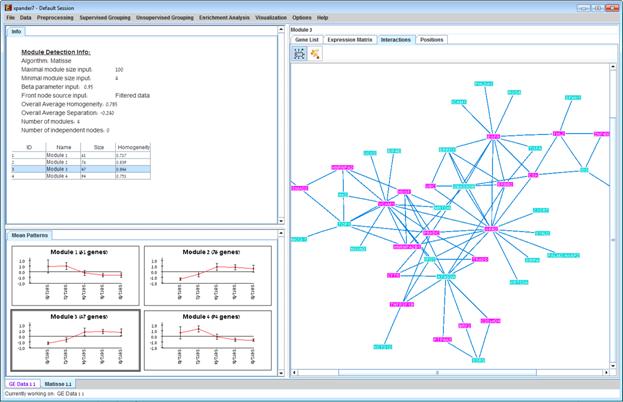
After running network-based clustering, the
solution is displayed in a new tab, which is added to the main window. The view
is similar to the clustering results display. However it contains an additional
interactions view tab for each module showing the sub-network that is formed by
the module. If the Cytoscape network analysis software is installed and is
running, it can be used for more advanced visualizations and analysis of this
sub-network by clicking on the Cytoscape tool-button (![]() ) placed at the top of the interactions
view tab. In the display, back nodes (genes that appear in the network, but not
in the GE data) are marked in pink.
) placed at the top of the interactions
view tab. In the display, back nodes (genes that appear in the network, but not
in the GE data) are marked in pink.
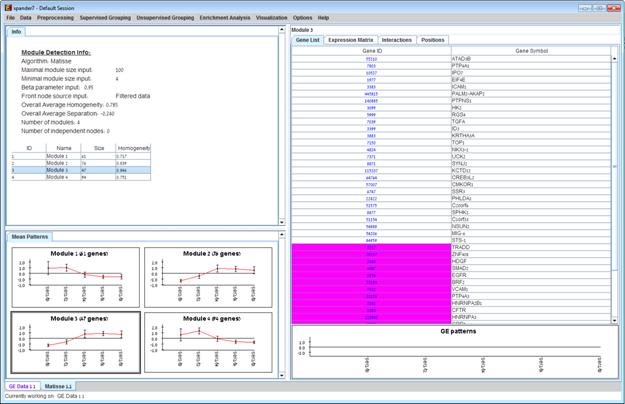
After performing enrichment analysis (for details see the Enrichment Analysis Tools section), if enrichment has been detected in the selected module, the corresponding histogram and analysis information are added to the single module view, and a column is added to the expression matrix display for each enrichment class, stating for each probe, whether it belongs to that class.
A network-based grouping solution can be saved using the File >> Export to text option (with the corresponding grouping view as the selected tab) OR by using the File>>Save All option, which will export all solutions within a session to text and image files. A network-based grouping solution can be reloaded using the Unsupervised Grouping >> Network >> Load Solution option or via Supervised Grouping >> Network >> Load Solution. For a format of the solution file, please refer to the File Formats section.