Yeast functional modules
and their transcriptional regulation
Database revision : gnsdb28.10
Date : Thu Feb 27 23:51:08 2003
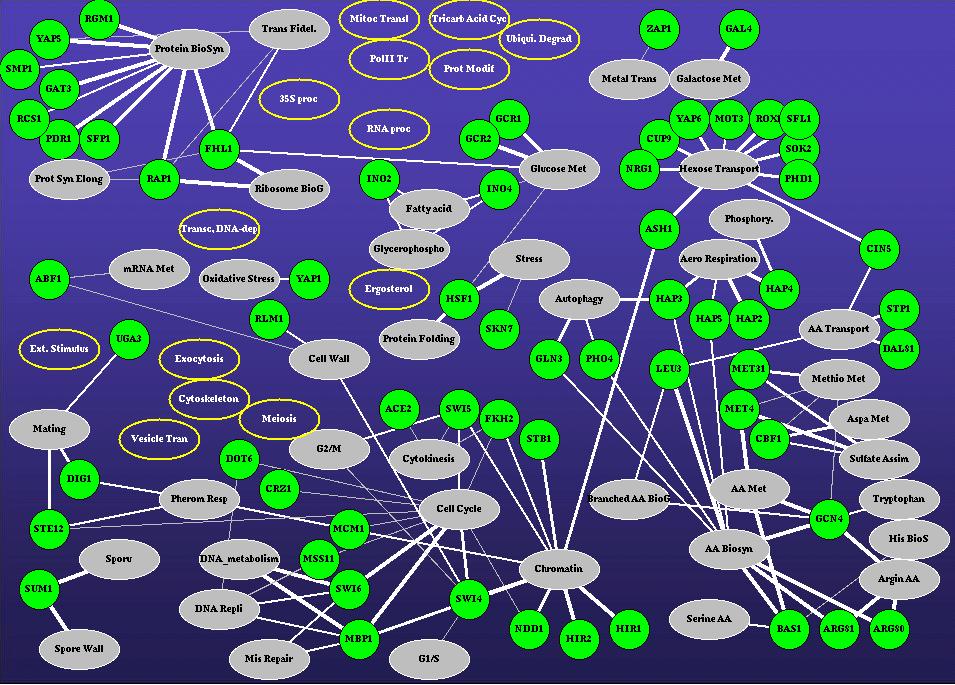
Functional modules and their transcription factors in the yeast
system. Modules with significant functional enrichment for a particular process
(p<0.01) are grouped and plotted as ovals with the process name. TFs with
binding profiles associated with any of these modules are marked as green
circles and connected to the associated process. Modules enriched in more
than one process may appear in several places in the figure. The thickness
of the connecting lines is inversely proportional to the p-value of the functional
enrichment in the associated module. The map was automatically generated
by SAMBA using no prior biological knowledge. Key abbreviations: Met:
Metabolism, AA: Amino Acid, Tran: Transport. Click a node for additional
information on the associated TF or process.
this is an automaticly generated
GENESYS report
Computational Genomics Lab, Tel-Aviv uniresity
